
Several natural and human-made factors have led to an increase in the occurrence of natural disasters. This has also surged the urgency for disaster risk-proof developmental initiatives to prevent social, economic, and environmental losses.
Globally, decision-makers are now planning and implementing various strategic actions and programs to reduce area vulnerability, build resilient livelihoods, and prepare for disaster events in the future. Integrating these strategies with the latest information technologies has become one of the central agendas toward disaster preparedness and sustainable development.
A similar technological intervention was planned recently for Jammu and Kashmir, considering its susceptibility to multiple natural hazards.
 Dwelling on Beauty as well as Vulnerability
Dwelling on Beauty as well as Vulnerability
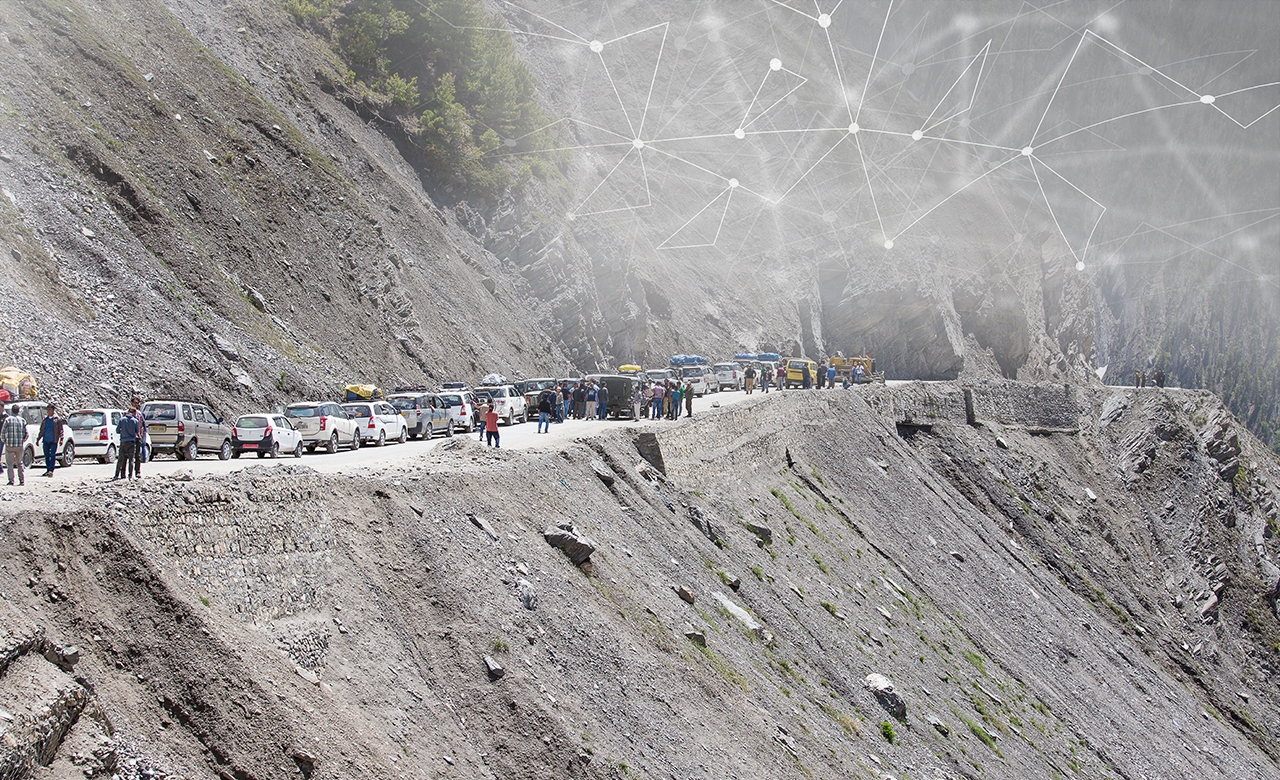
Jammu and Kashmir, prominent as the Paradise on Earth, is recognized for its mesmerizing beauty and rich flora and fauna. Despite being known for its pristine beauty, J&K also has a high vulnerability to natural disasters, including earthquakes, floods, landslides, avalanches, and snowstorms.
The Union Territory (UT) has a long drawn history of frequent natural and human-made disasters due to its peculiar physical setting and extreme weather conditions. Some of the major disaster events include snow blizzard at Waltengu Nad in February 2005, devastating earthquake in October 2005, cloudburst at Bagger in June 2011, and heavy torrential rains followed by catastrophic flood and landslide in September 2014.

Apart from causing colossal damage, the 2014 disaster had jolted the entire region and impacted more than 5 lakh people. Hence, the then Government of Jammu and Kashmir, along with the World Bank’s financial support, formed the Jhelum and Tawi Flood Recovery Project (JTFRP) in 2015.
The key objective of JTFRP is to restore the critical infrastructure to hazard-resistant standards, scale up the region’s capability to respond to an emergency, strengthen disaster risk management capacity through capacity building, and provide technical support for risk reduction and response preparedness through resilience action plans.
Assessing Disaster Risks to Formulate Strategic Actions
Quantification of risk is a critical and preliminary step towards disaster risk resilient planning. It is vital for mitigation planning, preparedness, and emergency response measures.
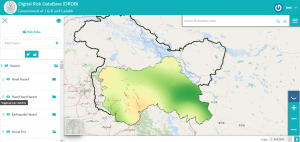
Considering J&K’s susceptibility to natural disasters, the government recognized the need for assessing the risks from natural disasters and development of risk database containing information of different disaster scenarios for hazards such as earthquake, landslide, flood, flash flood, avalanche, GLOF, forest fire, drought, climate variability, and industrial hazards.
Hence, RMSI is conducting the multi-hazard risk assessment for Jammu and Kashmir to develop hazard, exposure, vulnerability and risk information for various natural and human-made hazards.
The key deliverables include a Disaster Risk Database with a front end application that can be used to formulate an emergency response & mitigation strategy, and an Integrated Operational Forecasting System (IOFS) for the real-time warning on the flood, flash flood, and drought.
 Various training and capacity building sessions will be conducted after the study’s completion to capacitate various UT stakeholders on using risk information for multi-hazard disaster risk reduction. The study will help devise effective sectorial risk reduction strategies to ensure the UT’s sustainable development planning.
Various training and capacity building sessions will be conducted after the study’s completion to capacitate various UT stakeholders on using risk information for multi-hazard disaster risk reduction. The study will help devise effective sectorial risk reduction strategies to ensure the UT’s sustainable development planning.
Robust Platform for Real-time Project Management
The JTFRP has been executing numerous reconstruction projects as part of the Build Back Better strategy. The restoration initiatives include development and widening of access roads, construction and amenities improvement for hospitals, new schools, industrial expansion (silk emporium and willow factory) based on local resources, flood mitigation measures like dewatering stations, etc.
Around 170 projects are being implemented by different agencies and consultants across the UT.
With these ongoing developmental projects, it becomes practically impossible to manually track and monitor its schedule, effectiveness, and performance. To ease the project management process, JTFRP appointed RMSI to design, develop, and implement a comprehensive and robust web-enabled Management Information System (MIS).
 The cost-effective and user-friendly system helps the Project Implementation Units (PIUs) monitor the project’s physical and financial progress, and allows the PMU and the World Bank to monitor PIU or component-wise project progress for further disbursement of funds.
The cost-effective and user-friendly system helps the Project Implementation Units (PIUs) monitor the project’s physical and financial progress, and allows the PMU and the World Bank to monitor PIU or component-wise project progress for further disbursement of funds.
This system also provides transparency in public fund expenditure. It has a pubic grievance module which facilitates the public to submit any project related grievances to the PMU and World Bank. Also, it has a module to help generate project progress reports as per user specification.
Strengthening Disaster Risk Management Capacities
As part of its constant endeavor to reduce risks from disasters, the JTFRP is further strengthening the local capacity and capability of the Disaster Management, Relief, Rehabilitation and Reconstruction Department (DMRRR) and Jammu and Kashmir State Disaster Management Authority (JKSDMA) by developing a GIS-based state-of-the-art Emergency Management Decision Support System (EMDSS).
Currently, RMSI is developing EMDSS, which will eventually connect UT Emergency Operation Centres (EOC) at Jammu and Srinagar, District EOCs, and several field department control rooms (Police, Forest, etc.) to act as a team and share real-time information for integrated emergency management.
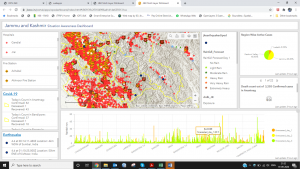 The DSS platform shall integrate real-time information from national and global sources, historical and baseline hazard, population, buildings, and infrastructure data with powerful analytics and decision support intelligence to offer a common platform to respond to disasters.
The DSS platform shall integrate real-time information from national and global sources, historical and baseline hazard, population, buildings, and infrastructure data with powerful analytics and decision support intelligence to offer a common platform to respond to disasters.
This is an ideal example of a holistic approach to disaster risk reduction.
The developmental initiatives commenced with Hazard Vulnerability Risk Assessment (HVRA) the outcomes of which were used for mitigation planning measures. There was initiation of the of mitigation plans in the form of retrofitting infrastructure projects. Furthermore, it focused on development of forecasting systems for hydro-meteorological hazards, and creation of a Decision Support System (DSS) for managing any future emergencies.
All these developments, coupled with a robust capacity building program, will help minimize the risk of the people of J&K from natural and human-made catastrophes. RMSI is proud to be a part of such a great initiative.