Research suggests that data quality is a single point of failure in today’s era of Artificial Intelligence. About 80% of a data scientists’ time today is consumed in ensuring that training data meets the defined quality standards that are required to be used in Machine Learning (ML) models.
Today, there are different types of annotation solutions such as bounding box, polygon, polylines, key point, and geo-spatial annotations. While basic annotation tools are appropriate for segregating between the different classifications, wherever analysis related to the proximity of different (mining) sites, agriculture, and infrastructure, is required, techniques like Geo-annotation come into play.
Let us understand Geo-Annotation better
Geospatial intelligence is gaining a lot of importance across industries. From being only used by government intelligence and military, now, it is being consumed in almost every domain ranging from national security to insurance, mineral exploration, land use and planning etc. The term geospatial data means, all kinds of data on objects and phenomena in the world that are linked with the earth, be it natural or man-made. For example, information on climate, roads, and soil but also maps or telecommunication networks. Using geospatial data with AI & ML tools, can do wonders for various industries and can lead us towards a more prepared future.

This is where Geospatial Annotation enters. The data collected by Satellite, GIS, Drone, etc. are annotated to create graphic models. This process involves annotating roads, water bodies, forests, agricultural lands, and deserts as a part of a machine learning (ML) exercise.
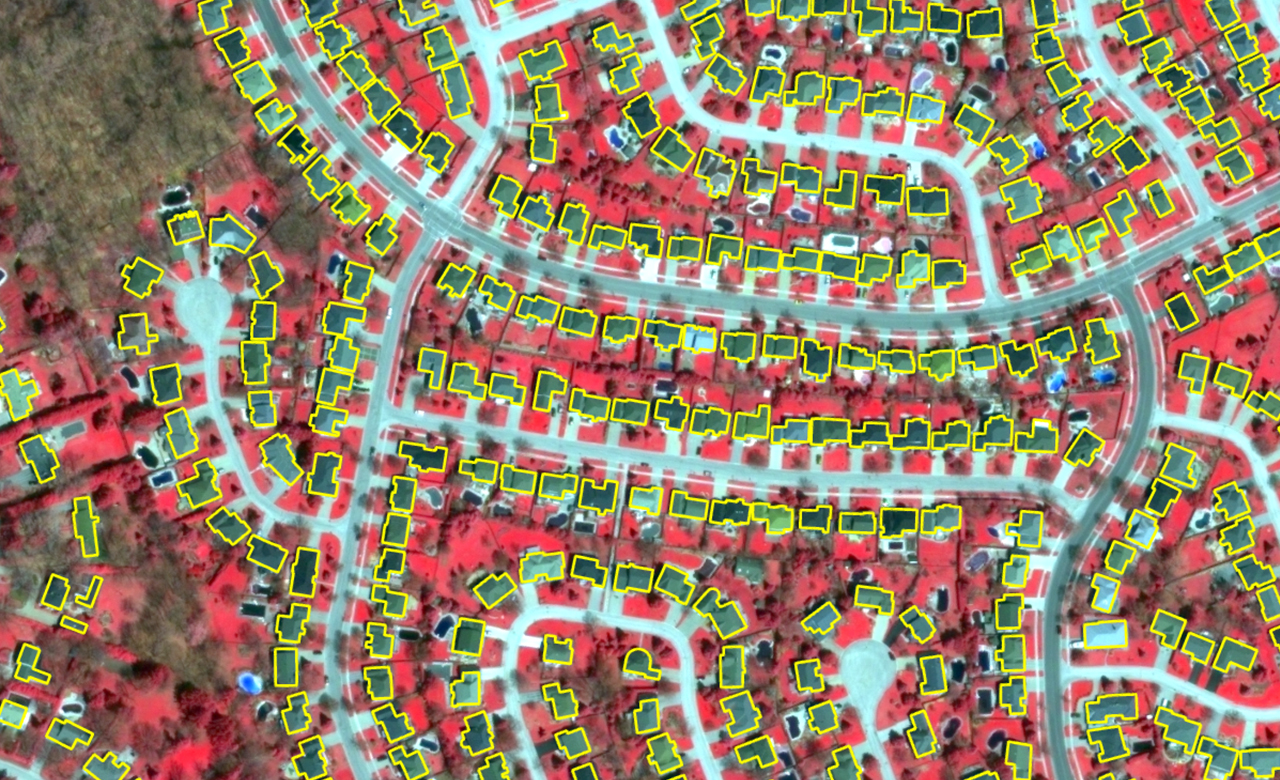
Geo-spatial Imagery Analysis
Geospatial Imagery analytics market was valued at USD 6.39 Billion in 2019 and is expected to reach USD 49.88 Billion by 2027.
Geospatial imagery, the “Visual Representation” of geographical features, is used to get video and image data of the Earth’s surface, using satellites and drones. In a nutshell, this is a snapshot of a particular area. When these imagery services are used simultaneously with GIS tools, it becomes a layer of information that is used to understand, visualize and illustrate the various geographical parameters. It is a tool that impacts almost every industry vertical.
Now, we can easily understand what Geospatial Annotation is – The creation of geographic models using remote sensing technology, such as satellite, aerial, and drone imagery, to produce and curate training data for machine learning and computer vision models across industries.
RMSI Geo Annotation experts utilize data acquired from Satellite, GPS, and Aerial Imagery (UAV’s) to annotate and create geographic models to produce training data for machine learning and computer vision models. We have the expertise of working with coarse to very high-resolution imagery using Remote Sensing, Photogrammetry, and LiDAR technologies.
Geo-annotation is useful for aerial view and drone imagery annotation, bounding box, semantic segmentation, etc.
Major application areas of Geo-Annotation
It may be a bit difficult to list out all applications of geospatial annotation, as we are using today, widely used applications by the industries are:

Agriculture
- Monitoring: For monitoring crop and soil conditions, geo-annotation is used to process the data captured by drones.
- Predictive Analysis: Weather conditions play a major role in crop yield. This technology is also helpful in tracking and predicting different environmental effects on the crop.
- Disease Detection: Due to the altering weather conditions, crops are very prone to diseases but with the help of geo-annotation, symptoms that appear at early stages can be easily detected.
Infrastructure Planning
- Roads detection: Satellite imagery analytics allows tracking the roads, constructions, and transporting schemas. Roads are easily detectable from above with only a 10-30 m resolution. AI models is used to track the network of roads, changes, new constructions. Distance of roads and networks about other assets (roads leading to flooded areas, or post-disaster evacuation, or urban planning) allows building informative analytics.
- Classification of lands: Rivers, lakes, streams, oceans, coastal boundaries, parks, land cover, and beaches can be easily identified using satellite imagery even at lower resolution. It is the common input used to reduce the area of interest in more insightful but requiring commercial high res imagery analytics.
- Building footprint: Recovery of the buildings with the help of satellite imagery can be used in various industries, such as land cover mapping, urban planning, disaster management, and extracting information about human settlement related to other economic activities.
Exploration of Resources
Geo annotation is now widely used in resource extraction, for analyzing the data related to breadth, depth, and frequency (from high-resolution satellite imagery to underground sensor data and surface mapping), we are now able to explore terrains that were impossible to access.
- Data Analysis: The data requires everything from natural topographical features, the presence of wetlands, migration patterns of wildlife, rivers, and other water bodies, for resource extraction.
- Analyzing the affecting factors: Factors like the mix of imagery, map, and 3D view of the mining site, environmental and regulation factors can affect planning.

In a recent project, our experts utilized satellite imagery for labeling and training a deep learning segmentation model for change detection of spatial features across the Persian Basin. This helped the client to successfully benchmark their ML model over 120 KM AOIs and TOIs with 99.9% accuracy.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has gradually moved on from mere theory to a wide practice. This has enabled digital transformation. These technologies allow us to carry out such tasks that weren’t possible a decade ago, enabling industries to simplify complex processes and scale their operations by gaining access to quality data and actionable insights. Geo-annotation can help in fostering growth towards a better tomorrow.