
In India almost 66% population lives in rural areas. The vital health services in these areas are provided by hospitals with emergency services and other small healthcare centers often serving as the foundations of rural health care delivery systems. Public healthcare is free for every Indian resident. But, long travel distance is one of the key challenges that rural citizens encounter to access and seek health care services in these nearby hospitals, as they normally serve multiple communities within a large region.
When a natural disaster, accidents, other emergency cases or disease outbreak occurs there is a rush to establish accurate health care location data that can be used to support response and recovery teams on ground. Access to healthcare is a requirement for human well-being that is constrained, in part, by the allocation of healthcare resources relative to the geographically dispersed human population.
At RMSI, we are committed to addressing global issues of human habitation, security & safety connected with food, calamities, use of natural resources. While assessing solutions to the above healthcare challenges, our mapping experts noticed that a lot of hospitals or healthcare centers didn’t even exist on most of the maps.
We believe strongly that the solution to most problems starts with getting the right data.
Map Intelligence with OpenStreetMap (OSM):
There are various online mapping platforms that provides mapping services across the globe, and one such popular open-source platform is OSM, a free and openly editable map of the world. OSM is a web-based public platform that collects data describing the position of roads, rivers, towns, point of interests, etc. used to create maps.
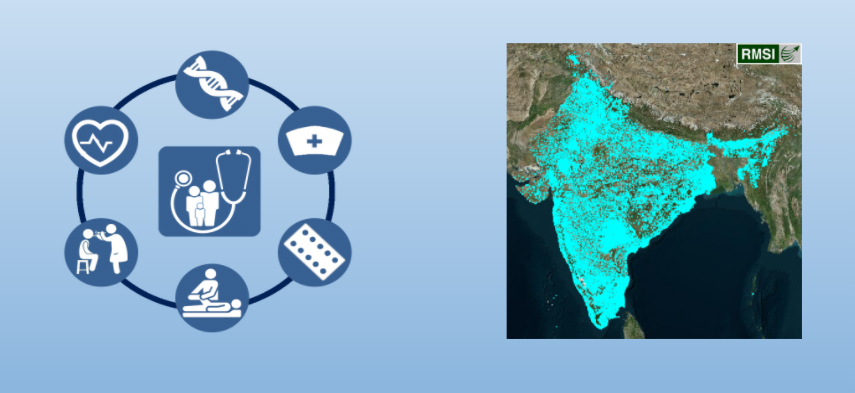
RMSI recently worked on enhancing the healthcare facility database in the country. The overall objective is to improve the Health facility POI in OSM data across the country (India) with the help of Government approved database and latest available imagery.
1. Data Resources
Our experts referred to the following open sources of data.
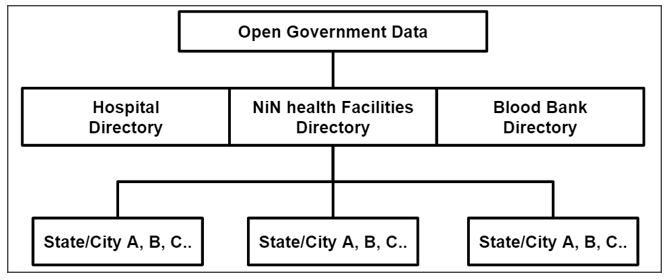
The OGD (Open Government Data) data was taken by the Government of the country or any government-controlled entities. https://data.gov.in is a platform that is supporting open data initiative of the Government of India.
“Open Data” platform is being offered to other countries and implemented in US as their data.gov. Few other countries are also being powered by Open data platform. Example: Ghana.
- OGD (Open Gov Data) – Hospital Directory
- OGD (Open Gov Data) – NIN Health facilities Directory
- OGD (Open Gov Data) – Blood banks Directory
2. OpenStreetMap – India Health Facilities Import Process
2.1 Process & Workflow
All the government datasets’ records are filtered and double-checked before importing in the OpenStreetMap. OSM Import guidelines have been followed while initiating the Health Facilities Import Process.
https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/India_Health_Facilities_Import
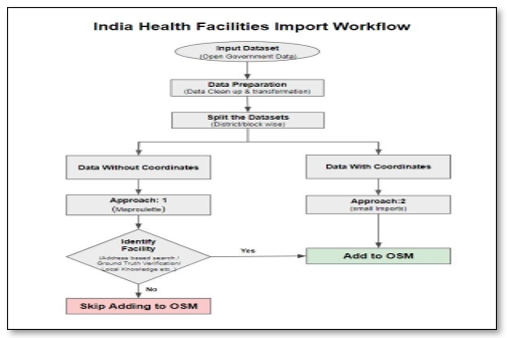
2.2 Data Preparation
In the first phase of the import process, RMSI team split each directories into small datasets based on States and cities of India.
The input data had few quality issues that were addressed immediately and further cleaned on the basis of values before the import. All the record of government datasets were ensured to be verified before importing into OSM.
The input data sets were further sanitized on the basis of
- Removal of invalid values – N/A, 0, /N, Blanks, etc.
- Cleaning of duplicates
- Proper transcription
- Convert the OGD attributes to OSM compatibility tag.
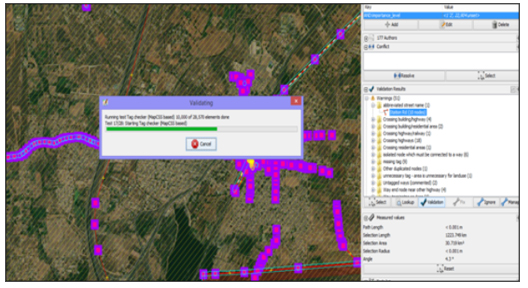
- JOSM validations were performed for cleanup of files and converted into geoJSON files before importing to OSM.
2.3 Data Execution
Every State Government’s hospital data was then revalidated and compared with the existing OSM data. The data import was performed using the import specific accounts and also by specific change set comments.
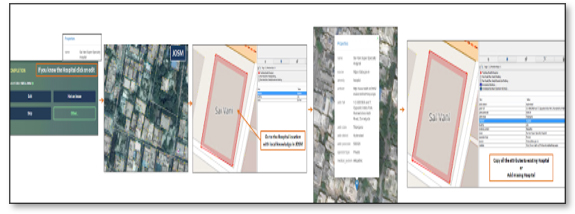
2.4 Quality Assurance
Conflation Tools were used to check for duplicates with the existing data and OGD data sets. Quality checks were performed using the JOSM tools before and after every import and was repeated for all the sub-datasets.
2.5 Smart Practices for Data Import
RMSI used Government approved websites to check for the available information on Health Facilities to ensure the completeness and quality of the data. A written checklist was followed by the team to ensure the quality and specifications were in met during production and review stage before the final delivery.
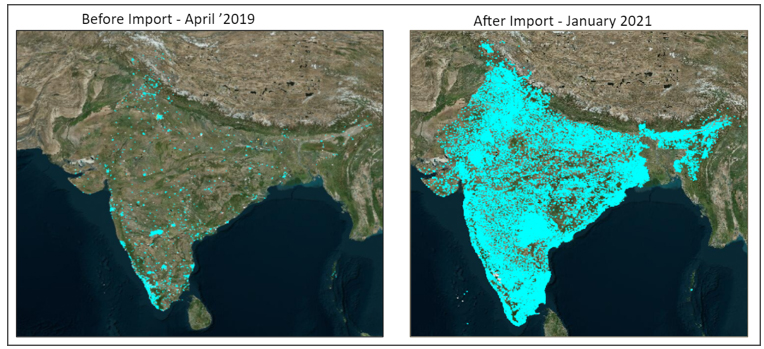
3. Health Facility POIs before Import & Current Data
4. Few Enhancements in Data
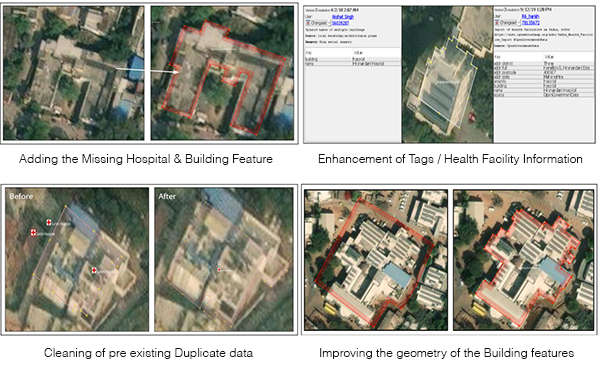
With the help of input data records (OGD), RMSI team added more valuable attributes to existing OSM data.
Example 1: Missing hospitals were identified and hospital/ building features were added in OSM data
Example 2: Existing hospital data was modified by adding all the proper tags and complete addresses to the health facility POI
Example 3: Duplicate entries were removed from existing data and corrected by cleaning up of duplications
Example 4: Building feature geometry was improved for existing data and tag correction was made as per OSM tagging guidelines.
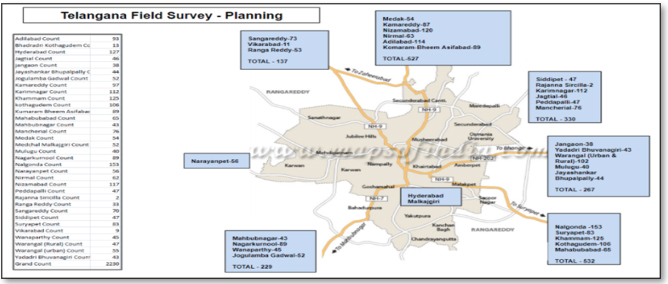
5. Field Survey for Telangana State
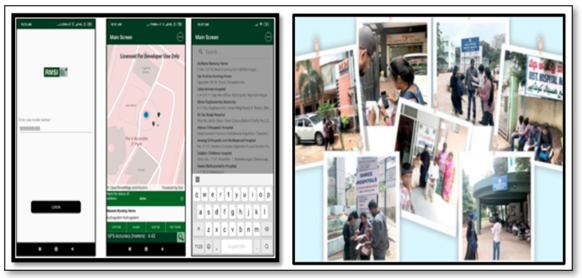
RMSI team first designed and developed an in-house application with customized functionality to fit our survey method. We then sorted all unsuccessful records district-wise and distributed them to each squad to collect locations of the remaining OGD data in Telangana. With the help of our application, our team captured the locations of the missing facility more efficiently and in a timely manner.
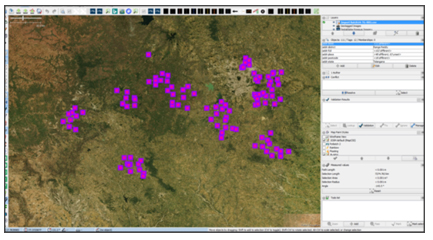
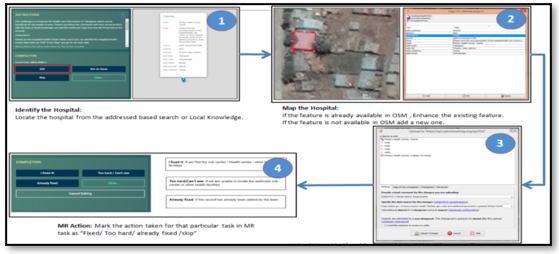
6. Map Roulette Challenges
With full support on the import from the OSM community, RMSI team initiated the import of the local regions, by creating Map Roulette challenges to verify the position of each data point from the cleaned and verified datasets.
RMSI also organized an OSM (OpenStreetMap) awareness program in December 2019, at Jawaharlal Nehru Government Polytechnic College in Ramanthapur, Hyderabad.
The goal of the workshop was to increase awareness about OpenStreetMap, its uses in times of a disaster or crisis management. It focused on how to reduce the disaster risk and enable a speedy recovery through these maps.
To spread awareness about OSM among college students, various GIS (Geography Information System) related activities were conducted to map the areas and places around the world. The workshop was held in two modules: OSM awareness training and OSM practical training, as highlighted in our previous blog Spreading Awareness About Mapping on OSM, a Free and Openly Editable Map of the World (rmsi.com).

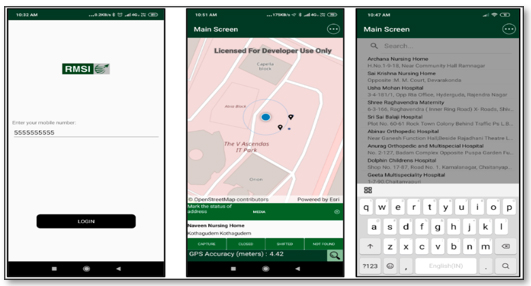
7. Survey Utilities
RMSI has developed an application to perform field survey for Telangana State.
8. Data Maintenance
As OSM is an open-source platform, there are always constant modifications required in data and frequent updates are required in real time. Hence, maintenance plays a prominent role for safeguarding the data. We use ArcGIS tool to constantly monitor the data and address all the new additions and deletion of existing health facilities. Maintenance team, simultaneously, validates the changes with all the available resources and make necessary changes.
Acknowledgments
RMSI is currently working to support expanded Information Management capacity within India. The project aimed to provide accessible data of accurate health care information from the Open Government Data directories for Hospitals, Health facilities, Blood banks, Health Centers and Health Clinics information which can be useful for all the people and also for Humanitarian causes. Core to the above goal, is also ensuring that this dataset of health facility data is easily accessible to everyone.
If you are interested in our progress, please keep watching the periodical updates on our import wiki. If you are interested in improving the health facilities in your local region please contact us at osm@rmsi.com so that we can share maproulette for your region.
Happy Mapping!